The COVID-19 epidemic began as a worldwide health emergency in late 2019 and swiftly grew to become one of the most ubiquitous problems of this day and age & today we will break down the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat really happens in Long COVID?
The primary cause of death due to COVID-19 is the occurrence of Acute Respiratory Failure caused by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Scientists have come across that the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 & the other members of the SARS family work by incarcerating the ACE2 enzyme that is the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 to enter the brain, heart, lungs & vasculature of the human body.
Symptoms of Long COVID
Patients with COVID-19 experience symptoms like dyspnea, hypoxemia, decreased lung compliance, airway resistance, brain fog & confusion, reduced diffusion capacity & deconditioning all of which impairs the quality of life. The comprehensive regimen of pulmonary rehabilitation incorporates patient education, aerobic exercise training, improvising the ventilation, inspiratory muscle training & airway clearance techniques to improve the respiratory

efficiency all of which can be achieved with the use of 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms.
Risk factors of Long COVID
The risk factors of long COVID are now gradually getting the attention they deserve. Out of all, the most important risk factor is having cardiovascular disease prior to getting COVID. Along with that, lack of vaccination, weak immune system, older age & poor mental health are also considered to be the high risk factors. Despite their seeming difficulty, these risk variables do not determine a survivor’s future health.
Why Pulmonary Rehab is essential after COVID recovery?
While we know how pulmonary rehabilitation can help you heal from COVID, let’s talk about the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms that you can implement at the present time. The unerring fitness regimen can make a big difference, whether you are battling chronic COVID symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, or decreased stamina, or you just want to regain your strength and immunity. In fact, research indicates that intensive physical therapy and breathing techniques enhance lung capacity while also increasing vitality, circulation, and general health.
If you’ve been wondering how to regain strength after COVID or what the finest post-COVID recovery workouts are, this article is just what you need to know about 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms. In order to prevent and fully manage deficits linked with acute or chronic pulmonary diseases, breathing exercises and ventilatory training are essential interventions. For scientific point of view read our article Proven Physiotherapy for COVID Recovery.
Following COVID-19, here are the 5 best exercises in pulmonary rehabilitation to recover from long COVID symptoms & help you breathe more effortlessly with strength & endurance progression:
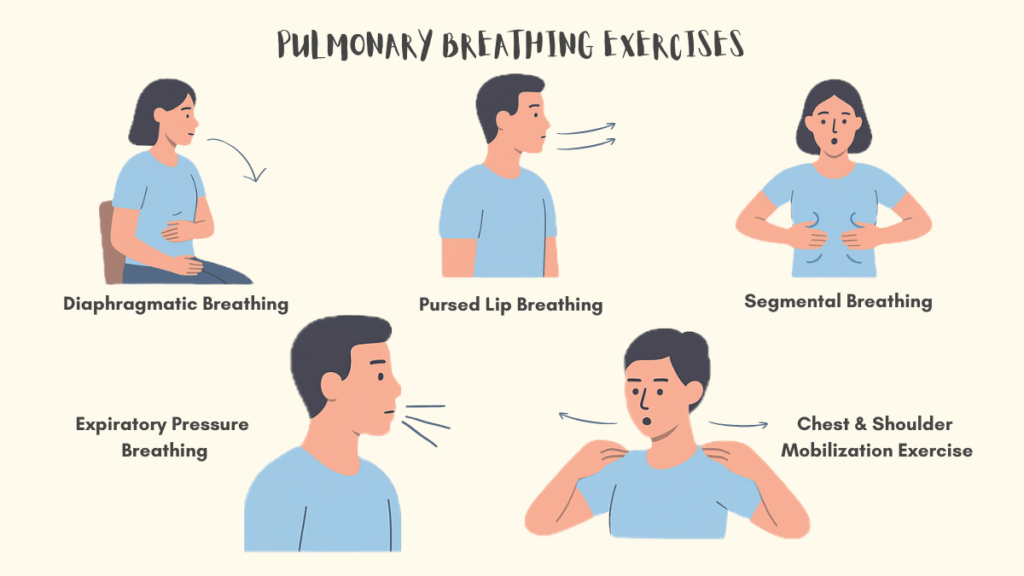
1. DIAPHRAGMATIC BREATHING
The very first exercise out of 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms is diaphragmatic breathing. The diaphragm’s efficient function as the main inspiratory muscle results in optimal ventilation and reduced oxygen use by the respiratory muscles during relaxed tidal breathing. But when a patient depends heavily on the accessory muscles of inspiration, the mechanical effort of breathing rises and ventilation efficiency falls leading to labored breathing.
As the accessory muscles attempt to draw the chest wall up to increase lung volume, the chest and rib cage may appear to collapse in between the ribs or behind the breastbone. Although breathing is involuntary, a patient with primary or secondary pulmonary impairment can still learn to control their breathing by using their diaphragm optimally.
Therapeutic Role
Why is diaphragmatic breathing one of the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms? This is because the main objective of controlled breathing strategies, such as diaphragmatic breathing, is to enhance gas exchange and oxygenation, reduce respiratory effort, increase diaphragm mobility, and optimize respiratory efficacy. Additionally, this breathing technique is employed to loosen secretions during postural drainage.
How to perform Diaphragmatic Breathing? Step by step guide:
- Position the patient in a relaxed alignment with a pillow behind his back such that the gravity supports the diaphragm i.e. Semi Fowler’s Position
- Rest your hand just below the costal arch on the rectus abdominis and ask the patient to take in long & deep breaths through his/her nose such that your hand lifts slightly in doing so.
- Ensure that the patient keeps his shoulders relaxed without any chest movement during breathing allowing the abdomen to lift your hand slowly.
- Then command the patient to exhale slowly through his mouth.
- In case of any trouble in engaging the diaphragm, ask the patient to rapidly inhale three to four times through his nose in order to stimulate the diaphragmatic activation. This method is known as Sniffing.
- For self monitoring purposes, have the patient place his hand below the costal arc and feel the movement pattern.
PRECAUTION
Complete 4-5 reps of this exercise & ask the patient to rest to minimize the risk of hyperventilation.
2. PURSED LIP BREATHING
The second approach in 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms is pursed lip breathing. Pursed lip breathing involves exhaling slowly while gently pressing the lips together, as if blowing a candle in front of you. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) frequently adapt this to manage dyspnea episodes. Pursed lip breathing helps to maintain open airways by generating back pressure in them, which lowers respiratory rate and respiratory effort while increasing tidal volume.
Therapeutic Role
By retaining airways accessible for longer periods of time and limiting air trapping, pursed lip breathing enhances ventilation. It encourages deeper, more deliberate breathing, which reduces anxiety and dyspnea. This helps promote oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, enhancing total lung efficacy making it one of the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms.
How to perform Pursed Lip Breathing? Step by step guide:
- Place the patient in a relaxed & comfortable position.
- Ask the patient to breathe in slowly & deeply through his nose & then breathe out from his mouth as if he is blowing a candle.
- Ensure that the patient performs expiration in a relaxed state & doesn’t contract his abdominals for support.
PRECAUTION
Forceful expiration should be avoided during pursed lip breathing as it can increase non laminar flow in the airways.
3. SEGMENTAL BREATHING
The question of whether a patient may actually upskill to expand certain localized lung regions while maintaining tranquility in other parts is frequently disputed. These 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms aren’t just about robustness, they also prevent injuries. Nonetheless, studies and clinical data verify that hypoventilation does happen in discrete lung segments as a result of conditions including pneumonia, atelectasis, muscle guarding, post operative discomfort, and chest wall fibrosis. It becomes crucial to highlight the expansion of certain lung regions with segmental breathing exercises in various circumstances, such as during postural drainage or following thoracic surgery.
Therapeutic Role
Following COVID-19, many patients carried stiffness, decreased lung capacity, and poor oxygen exchange. Segmental breathing is important in this situation because it helps direct airflow into areas of the lungs that are inadequately ventilated, enhances alveolar recruitment, and encourages better oxygenation and lung compliance. Physiotherapists can speed up post-COVID pulmonary rehabilitation by following these 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms, lower the risk of secondary infections, and improve overall pulmonary function by teaching patients to expand particular lung segments.
How to perform Segmental Breathing? Step by step guide:
- In case of Lateral Basal Expansion, start with dorsal recumbent position & later progress to sitting.
- Rest your hands against the lateral aspects of the lower ribs region to help the patient concentrate on the lung segment that needs targeted expansion.
- Ask the patient to exhale while observing the ribcage moving downward & inward.
- As exhalation occurs, apply gentle pressure to the lower ribs with the palms of your hand in order to facilitate controlled breathing.
- Stretch the chest wall swiftly downward and inward right before inspiration. This helps facilitate the contraction of external intercostal muscles & enhances chest expansion.
- To improve perception of sensation, apply a small amount of manual resistance to lower ribs as the patient inhales deeply.
PRECAUTION
The patient should avoid breathing too fast or too deep in order to prevent hyperventilation. Ensure the patient is in a comfortable position prior to the performance of this exercise to prevent muscular strains.
4. EXPIRATORY PRESSURE BREATHING
In expiratory pressure breathing, the resistance to airflow is applied in exhalation with a specialized mouthpiece or mask. This helps hold the airways open during expiration & aids in secretion mobilization.
Therapeutic Role
It also helps re-inflate the collapsed alveoli, enhances oxygen uptake, reduces air trapping, & gives patients a sense of breathing control. It also reduces the chances of secondary infections such as pneumonia making it one of the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID.
How to perform Expiratory Pressure Breathing? Step by step guide:
- Adjust the patient to an upright posture ideally when seated with elbows resting on a table.
- This breathing technique can be carried out under high as well as low pressure.
- Low pressure technique involves active expiration through the mouthpiece but not forced.
- Ask the patient to inhale gently & hold the breath for 2 to 3 seconds & then exhale.
- Repeat the process for about 10 to 15 cycles.
- To clear out the secretions; ask the patient to remove the mask, huff for 3 to 5 times & then cough effectively to expectorate the secretions.
PRECAUTION
Always ensure the patient tolerance prior to this exercise & discontinue immediately if the patient reports chest tightness, excessive fatigue or increased dyspnea instead of relief.
5. CHEST & SHOULDER MOBILIZATION EXERCISE
Any type of exercise that incorporates deep breathing with dynamic trunk and extremity maneuvers is considered a chest mobilization exercise. They are made to keep the shoulder girdles, chest wall, and trunk mobile when ventilation and postural alignment are impacted. These exercises are also employed to support regulated expiration or the depth of inspiration. This is why this exercise is one of the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms.
Therapeutic Role
By combining the chest mobility exercises with deep breathing we can enhance chest wall flexibility as they may help mobilize the stiff costovertebral & costosternal joints. It also helps in improving the tidal volume & ventilation-perfusion matching. Exercises for chest mobility offset the effects of extended hospitalisation or bad posture. It facilitates more effective breathing dynamics by improving the alignment of the spine and thorax.
How to perform Chest & Shoulder Mobilization Exercise? Step by step guide:
- Ask the patient to comfortably sit on a chair with hands interlaced behind his head.
- Now ask the patient to breathe in deeply with having him abduct his arms to elongate the pectoralis major.
- When exhaling, ask the patient to bring the elbows together & downward with flexing your chin.
PRECAUTION
Avoid excessive trunk & ribcage movements to prevent pain & injury. Ensure the exercises are performed in a proper upright, supported or semi fowlers position to avoid strain.
NOTE: This blog has been written by a professional Physiotherapist with years of clinical experience in rehabilitation. Always consult your physical therapist or medical specialist if your symptoms worsen, or if you experience pain, dizziness, or difficulty while performing these exercises. Safety first!
The role of COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY in recovering Long COVID
Along with 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms, cognitive behavioral therapy can play its role too. CBT is a type of psychological treatment that is used to treat a diversification of issues, such as serious mental illness, eating disorders, alcohol and drug abuse, depression, anxiety disorders, and marital issues. Several findings stipulate that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) significantly improves functioning and quality of life hence can be used as a supportive strategy in managing long COVID symptoms. With long COVID, many individuals face difficulty with persistent symptoms such as anxiety, exhaustion, mental fog, confusion, lethargy & disrupted circadian cycle.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) assists people in uncovering detrimental mental habits that could exacerbate symptoms and substituting them with more positive, healthy ways of thinking. CBT is effective in boosting mental resilience, encouraging healthy lifestyle changes, and aiding in overall recovery, even though it might not be able to completely eradicate all of the physical effects of Long COVID. But the study of CBT is significantly more extensive, and the implications go far deeper than Long COVID. Investigating the ways it works in various medical disorders may lead to even more opportunities for recovery and overall wellness.
A guide to Long COVID Survivors
It takes proactive measures to regain strength, lung capacity, and quality of life after COVID-19. Recovering from the virus involves more than just anticipating time to pass. It has been experimentally demonstrated that these five straightforward yet efficient physiotherapy breathing and mobility exercises promote post-COVID recovery, enhance oxygenation, and lessen chronic issues hence known as the 5 best exercises to recover from long COVID symptoms. The secret is consistency; even a short everyday session can have a significant impact on your lung recovery. To learn more watch Top 10 Pulmonary Rehab Exercises to Do at Home to Improve Lung Capacity
Nonetheless, each patient heals at a unique timeframe. If you’re doubtful where to start or want a personalized program for your recovery, don’t hesitate to take help from the professional. Book your online consultation now by leaving a comment below or through our contact us page to get a tailored recovery plan that’s safe & effective to follow with daily progress monitoring.
