What is Stroke?
A stroke is the abrupt loss of brain function brought on by a disruption in blood flow. It is one of the leading causes of long term disability in individuals around the globe. While rehabilitation is the answer to its recovery, it has some new forms that are used now to move towards healing. Virtual reality has now taken over many aspects of healthcare including Physiotherapy. Let’s unveil the truth about VR in stroke recovery.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Physiology of Stroke
Stroke patients exhibit a wide range of behaviors and approaches to information interpretation. Understanding these patterns is necessary before discussing any treatment regimen especially when talking about the truth about VR in stroke recovery. Individuals with left hemisphere lesions, namely those exhibiting right hemiplegia, exhibit challenges in communication and in the logical, linear processing of information.
They are frequently described as nervous, anxious, and fogged. People who have lesions in their right hemisphere, those exhibiting left hemiplegia, have trouble with spatial-perceptual skills and understanding the primary concept of tasks and activities.
The incidence of visual perception impairments following a stroke has been found to range from a record high of to more than forty percent. They are more common in left hemiplegia than right, and are often caused by lesions in the right parietal cortex. These could include inability to interpret sensations & recognize things, spatial relations, and abnormalities of physical perception and pattern. By encouraging activity and reducing deficiencies in bodily functions, rehabilitation plays a significant part in boosting involvement in community tasks.
Everything you need to know about the truth of VR in Stroke Recovery
Virtual reality is quickly becoming a potent physiotherapy contraption that is transforming how patients heal from musculoskeletal and neurological disorders. VR provides a realistic engaging experience that makes patients intrigued and involved, in contrast to conventional rehabilitation techniques. Patients can safely rehearse movements, balance, and coordination while getting immediate feedback through gamified activities and tailored virtual surroundings.
With this forefront method, physiotherapists may more precisely monitor patient development and modify therapy regimens in response to specific requirements. Virtual reality is becoming more affordable and accessible as technology develops, & the truth about VR in stroke recovery is the topic which will make it a viable complement to contemporary physiotherapy clinics.
So how does Virtual Reality help in the Recovery of patients?
By giving patients and their families clear instruction, education, and training, physical therapists play a cardinal role in stroke rehabilitation. Asking straightforward yes/no questions, speaking in a relaxed, everyday tone, and, where applicable, utilising gestures or tactile signals to improve comprehension and engagement are all crucial components of effective communication. One of the ways to assist the patient through tactile cues involves the use of virtual reality.
The Role of VR in Walking training
VR video games enable walking training by simulating actual world settings. Walking visualisation has been examined at both the task and strategy levels. In terms of strategy, people who had a stroke pictured walking and altering the kinematics and kinetics of their motions, such as loading the injured lower extremity and taking a bigger stride with it. The speed and gait pattern can be improved with this kind of training. This covers an important aspect of the truth about VR in stroke recovery.
The phenomenon of Neuroplasticity
When talking about the truth of VR in stroke recovery, we must look into the phenomenon of neuroplasticity. During an analysis, at task level training, post stroke patients were encouraged to visualize themselves walking in different landscapes with the attention to assigned work. This helped in enhancing their neuroplasticity, that is, the brain’s capacity to heal and restructure itself following damage, developing motor control, building confidence & training attention span of the patient all along with task centered learning to improvise the daily activities of life. VR can further boost involvement in group therapy situations by encouraging friendly competition or teamwork.
When performing certain tasks repeatedly during rehabilitation, the brain starts to develop & build new healthy connections with the body hence rewiring the memory. It also begins to use the healthy parts to more extent for functional capabilities than the damaged area. People can become more mobile and independent by updating skills and adjusting to new methods making neuroplasticity an important aspect in stroke recovery.
Rebuilding Balance with VR
VR, including video games on the Nintendo Wii console and commercial and customized virtual environments with targets, has recently been studied for the rehabilitation of postural control and activity level balance. Patients can practise balancing exercises in a secure setting by using these virtual reality platforms, which mimic daily life situations and tasks that test postural control. VR encourages better coordination, core strength, and postural stability by putting patients through interactive exercises including weight shifting, reaching, and stepping. One of VR’s main advantages is its instantaneous visual and aural input, which enables patients to make current time movement corrections.
Exploring the Scientific data
As additional research demonstrates quantifiable improvements in motor function, clinicians are starting to recognize the truth about VR in stroke recovery.
A 2024 study, Effects of virtual reality on stroke rehabilitation published in Health Science Reports found that virtual reality significantly improved balance and motor recovery in stroke patients.
Hao, Crum, and Siu conducted an umbrella review to evaluate the effects of virtual reality (VR) on several areas of stroke recovery. They did this by analyzing evidence from 78 systematic studies, including 55 with meta-analyses. The authors used the AMSTAR‑2 program to evaluate the methodological quality of each review after searching five major databases through December 2023.
{Researchers utilize AMSTAR-2 to assess the quality of systematic reviews, which are studies that compile and examine a large number of other studies.}
The majority of reviews indicated that VR was more beneficial than traditional therapy across a range of outcomes, including upper limb motor skills, balance, basic mobility, pace of walking, independence in daily activities, and cognitive function. Nevertheless, there was conflicting data about cognitive and engagement results, and several of the included evaluations received low or very low quality ratings.
All things considered, what really is the truth about VR in stroke recovery? Well, the answer is quite simple. VR seems to improve recovery in physical functions, especially in both upper and lower extremities, gait, and balance, whether it is employed alone or in conjunction with conventional rehabilitation. While the conventional rehabilitation covers all the widely accepted & traditional methods of recovery, VR is a bonus addition to it. The authors stress that in order to improve the quality of the evidence, future research must have a stronger design and follow systematic review criteria indicating that there is a gap that should be studied prior to the conclusion of the use of VR as a rehab tool.
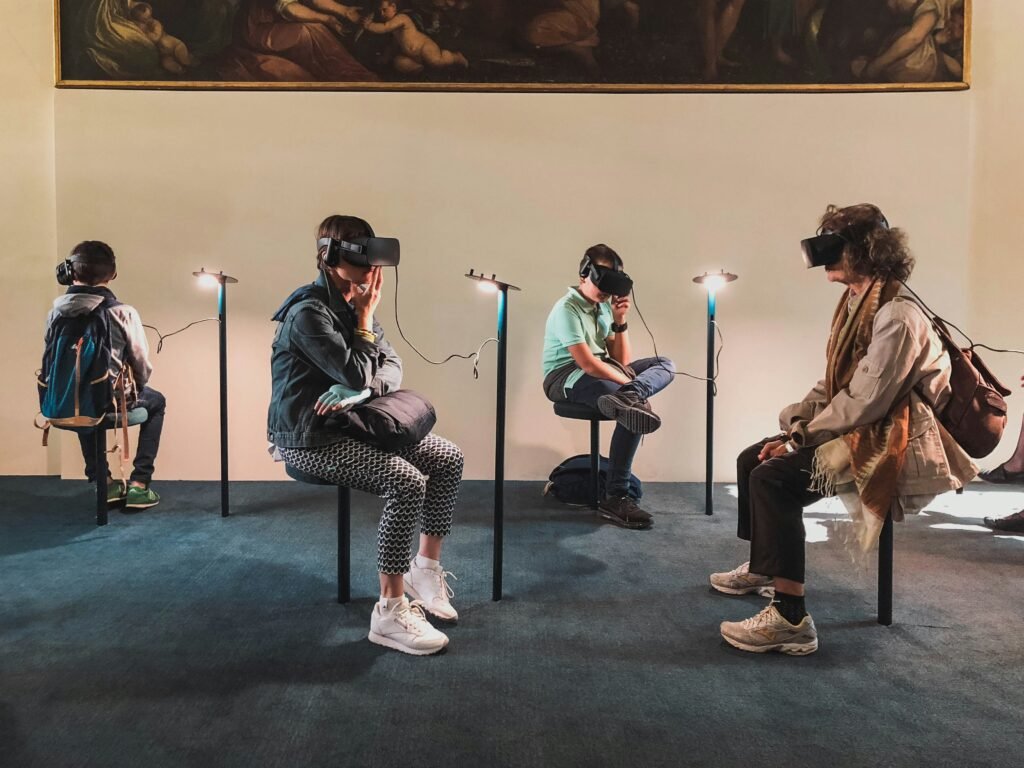

Another study on the application of virtual reality in the home environment was carried out to understand the truth about VR in stroke recovery with stroke patients. Walking both within and outside the dwelling was part of the participant individualized therapy. After watching the task being completed, the therapist modified the cues. The cues were intended to enhance both movement and gait pattern effectiveness. When the participants were seen climbing stairs, it was observed that the patient used virtual reality to accommodate himself by handling the banister, thereby reducing the chance of falling.
The use of virtual reality to enhance balance and gait training has so been supported by a few, but consistent, studies. Furthermore, VR’s games boost patient engagement and motivation, which improves the fun and efficacy of rehabilitation. The degree of difficulty can be changed as patients advance to accommodate their skills, guaranteeing ongoing gains in confidence and balance while performing daily tasks. This gives us a new divulgence when discussing the truth about VR in stroke recovery.
Role of VR in Speech therapy
In the past few years, the use of up to date technologies , especially after the pandemic COVID-19, has become the new answer to many questions. Read more about COVID in our blog Proven Physiotherapy for COVID Recovery. This initiative is proving to be time effective for stroke patients as well. Certain virtual reality apps have been made that help the patients to cope up with their language impairments, as well as providing computer based artificial environments to deal with their anxiety.
Other VR tools that are accessible especially for speech rehabilitation; they provide interactive activities that assist patients practice verbal communication in natural settings, word recalling information, and sentence construction. After a stroke, patients may gradually improve their language comprehension and speech clarity thanks to these immersive surroundings that lower anxiety and give them a safe, encouraging atmosphere in which to practise speaking.
The Challenges of VR
When unveiling the truth about VR in stroke recovery, let’s not forget its drawbacks. One of the major challenges with this technology is that certain systems are not accessible in clinical settings. Following VR sessions, some patients may feel drowsy or nausea, especially in intensely immersive settings. Some individuals may experience rebound trauma or worsen their dread or paranoia as a result of VR’s anodyne nature. But this is a field that is developing quickly, and technology is moving into clinics faster than previously thought.
What will be the future of VR in Rehab?
Future technology might incorporate artificial intelligence driven adaptive therapy, in which exercises change autonomously according to patient performance thus supporting the truth about VR in stroke recovery even further. Temporal feedback devices, which mimic pressure and touch, have the potential to improve motor learning by adding a new level of realism to VR rehabilitation. In addition to this, the use of Augmented reality, which superimposes virtual features on the physical world, is gaining popularity and may provide novel approaches to patient training in authentic settings.
Virtual reality is not simply a trend; it is a paradigm shift in the way rehabilitation is provided, providing hope for quicker, more successful recovery outcomes by simulating everyday life obstacles in a controlled environment.
This article has been written by a Physical Therapist and provides general guidance on physical health & exercise. While it is grounded in professional expertise, it is not a substitute for individualized medical advice. If you are experiencing pain, specific symptoms, or have an underlying medical condition, please book a 1 on 1, 30 minute consultation with our expert physical therapist for a personalized assessment & tailored recommendations.

Pingback: AI Devices as an Investment in Cardiac Rehabilitation